Roads & PavementRoads & Pavement
Barefoot
Minimal
Low
Medium
High
Maximal
All around running shoes offer comfort and cushioning for daily runs, jogs, walks, and long mileage. They offer enough versatility for both faster and slower runs and are a great option for those who want one running shoe to do it all.
Fast run or uptempo running shoes are lightweight and responsive. They offer streamlined designs that have minimal uppers and offer a high level of energy return. These shoes are a great option for faster runs in the week or those looking for a livelier experience.
Max Cushion shoes offer premium cushioning with ample ground protection and a stable ride. These types of shoes provide abundant impact protection that softens landings while running at any pace or distance. These types of shoes are best for slower recovery runs and easy days where comfort takes priority.
Racing shoes are designed with optimal performance in mind. These types of shoes have snug-fitting uppers, energetic midsole foams, and features implemented for maximum efficiency. These types of shoes are best for runners looking to gain the ultimate advantage in races but may sacrifice some durability and comfort.
Gym Workout shoes offer a stable and versatile ride. They have a firmer underfoot feeling that provides stability for lateral movements with comfortable uppers. These types of shoes are best for trips to the gyms, cross training, casual wear, and light running. Belt Drives Types Slip Creep Advantages Disadvantages PDF
Road running shoes feature smooth outsoles that are designed for running on paved surfaces such as roads, sidewalks, and bike paths.
Designed to handle most trail runs, these shoes prioritize comfort and a smooth ride. These shoes are great for anything from smooth singletrack, park trails, and fireroads making them ideal for those who run from their doorstep on streets before hitting the trail.
These shoes are best used for hard, rugged trails such as shale, granite or sandstone where grip on smooth surfaces and underfoot protection are important.
Designed for use in muddy, soggy conditions, these shoes feature very aggressive outsoles that dig deep into soft ground for exceptional traction.
These shoes feature technical outsoles designed to grip snowy and icy trails making them ideal for winter trail running.
Cushioning level, or stack height, refers to how much shoe is between your foot and the ground. For this category, we reference the amount of cushioning below the forefoot as the heel height will be equal to or greater than the forefoot height.
Basic Pulley Mechanisms 17 Steps with Pictures Instructables
0-13mm. The Shoe generally does not have a midsole and feels like there is no cushioning. This shoe is all about feeling the ground underfoot.
14-18mm. The shoe has a thin midsole that allows for a natural running experience. Racing shoes and minimalist shoes are common here. These shoes offer a feeling of being connected to the road or trail.
19-23mm. The shoe has a slightly cushioned feel and may feature added cushioning technologies. Performance training shoes and some trail shoes are common here. These offer protection during footstrike but prioritize a lightweight, grounded experience.
24-28mm. These shoes have a stack height that fall near the middle of the spectrum.The shoes in this category are verstaile and great for all types of runs and distances.
29-34mm. The shoe has a thick midsole and ample cushioning. These shoes are highly protective and absorb more impact than the body.
35mm plus. The shoe has an extremely thick midsole and extra cushioning. The focus is on protection and soft foam underfoot with hardly any ground feel.
Neutral shoes support the foot through a normal range of arch collapse and generally do not have a built-in technology to correct movement.
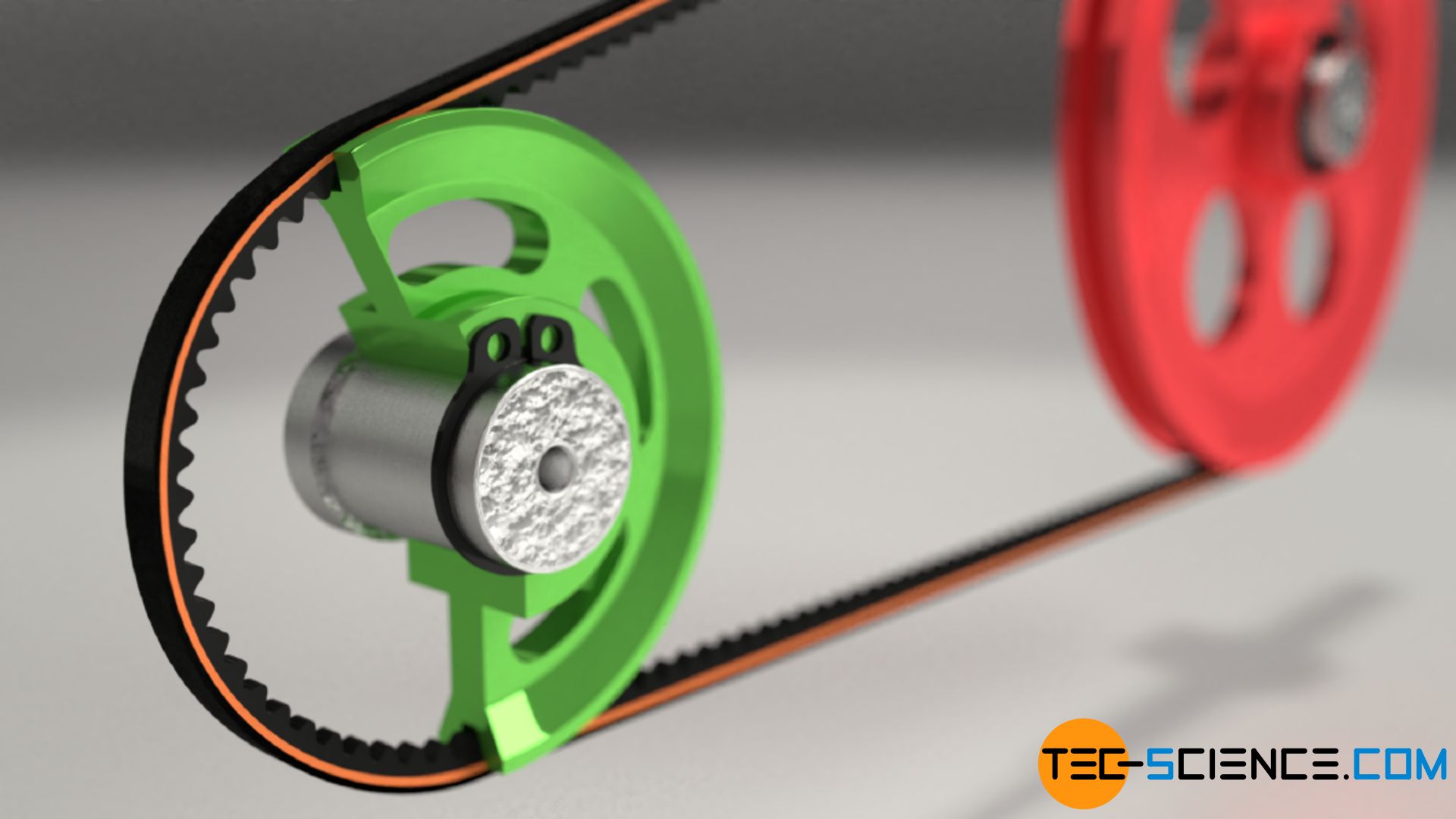
Stability shoes are a great option for those who overpronate or need added support. These shoes help to limit the inward rolling motion of the ankle while running or walking and assist in guiding the foot straight through the gait cycle. Types of belts for belt drives tec science
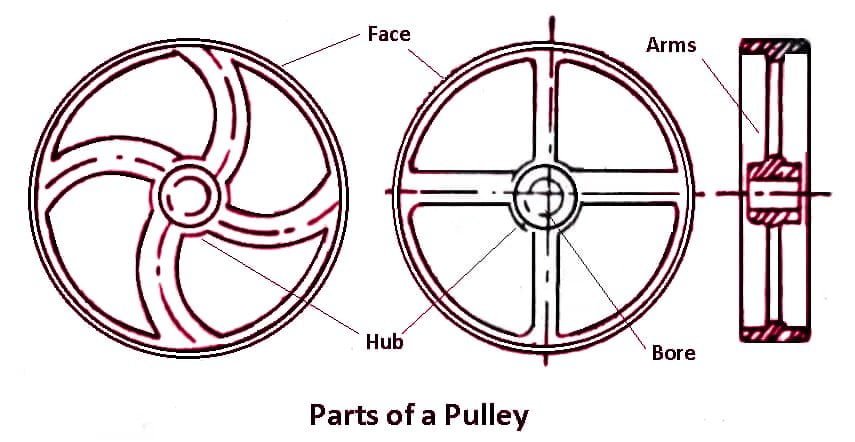
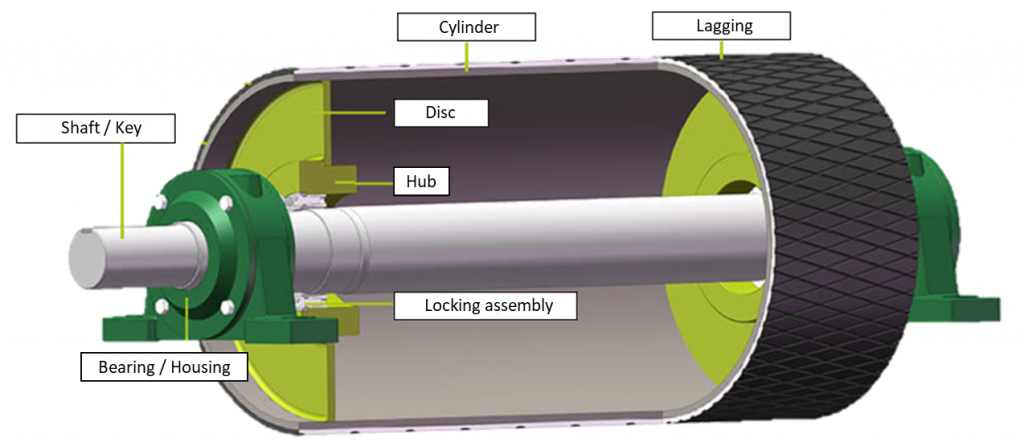
Product Details:
Belts and Ropes Definition The belts and ropes are used to transmit power from one shaft to another by means of pulleys which rotates at the same speed top, Belt Drives Types of Belts Fractory top, Alternator Pulley design and function. A little basic information top, Belts Chains UNC Charlotte Engineering Tool Kit top, The pulley paradox How to Spot a Psychopath top, V Belt Pulleys Definition Types Uses Application More top, Mechanics Map Belt Friction top, What s the importance of proper depth of engagement between a belt top, V Belt Tensioning Tameson top, Belt and Pulley Systems PDF Belt Mechanical Machines top, What is Flat Belt Drive Its Advantages and Disadvantages top, Belt Conveyor Pulleys What are they and its importance Kot top, Types of Pulley Definition Uses Diagram Examples top, Types of belts for belt drives tec science top, Basic Pulley Mechanisms 17 Steps with Pictures Instructables top, Belt Drives Types Slip Creep Advantages Disadvantages PDF top, Belt Drives Types of Belts Fractory top, What is a pulley on a car What is its function Quora top, Robotic Mechanisms PULLEYS and BELTS 51045 Robotpark ACADEMY top, Belt Features in Mechanism Design PTC Community top, Timing Pulleys Idler Pulley Single Double or No Flange Pulleys top, Belts AND Pulleys BELTS AND PULLEYS Definition of Terms Belt is top, Difference Between Flat Belt Drive and V Belt Drive top, What is the difference between a driver pulley and a driven pulley top, How to account for belt and pulley inertia during system design top, Design of Belt Drives With Pulley Theory By Prof. Sagar A. Dhotare top, Belts AND Pulleys BELTS AND PULLEYS Definition of Terms Belt is top, What is a Timing Belt Pulley Illinois Pulley Gear top, Pulleys Beginners Guide Basics of conveyor pulleys top, Robotic Mechanisms PULLEYS and BELTS 51045 Robotpark ACADEMY top, V Belt Drive Advantages and Disadvantages top, Types of Belt Drive Material Applications Advantages top, Belt Drives 1.pptx top, Differences between Belt Drive and Chain Drive MechanicalEngineering4u top, SOLUTION Definition of belt and pulley Studypool top, Timing Belts Design Types Applications and Advantages top, Seven pulley serpentine belt drive example defined in Table 1 top, What is Belt Drives Type Advantages and Disadvantages top, Pulley balancing for belt drive systems is it always necessary top, V Belt What Is It How Does It Work Types Of Uses top, How does a belt drive work tec science top, 10 belt and pulley mechanism examples Mechanicaleng blog top, Round Belt Pulleys Selection Guide Types Features Applications top, Belt mechanical Wikipedia top, Robotic Mechanisms PULLEYS and BELTS 51045 Robotpark ACADEMY top, Pulley Systems 1 top, What is Belt Drives Type Advantages and Disadvantages top, How does a belt drive work tec science top, Belt pulley definiton functions types parts working top, Pulley Wikipedia top, Product Info:
Belt and pulley definition top.
- Increased inherent stability
- Smooth transitions
- All day comfort
Model Number: SKU#7011133